電話:021-69515711
電話:021-69515711 手機:13818065015
手機:13818065015 傳真:021-69515712
傳真:021-69515712-

 1049485
1049485
-

 8459743
8459743
-

 1993509414
1993509414

 :renrimarket
:renrimarket 
 market@renri.com.cn
market@renri.com.cn
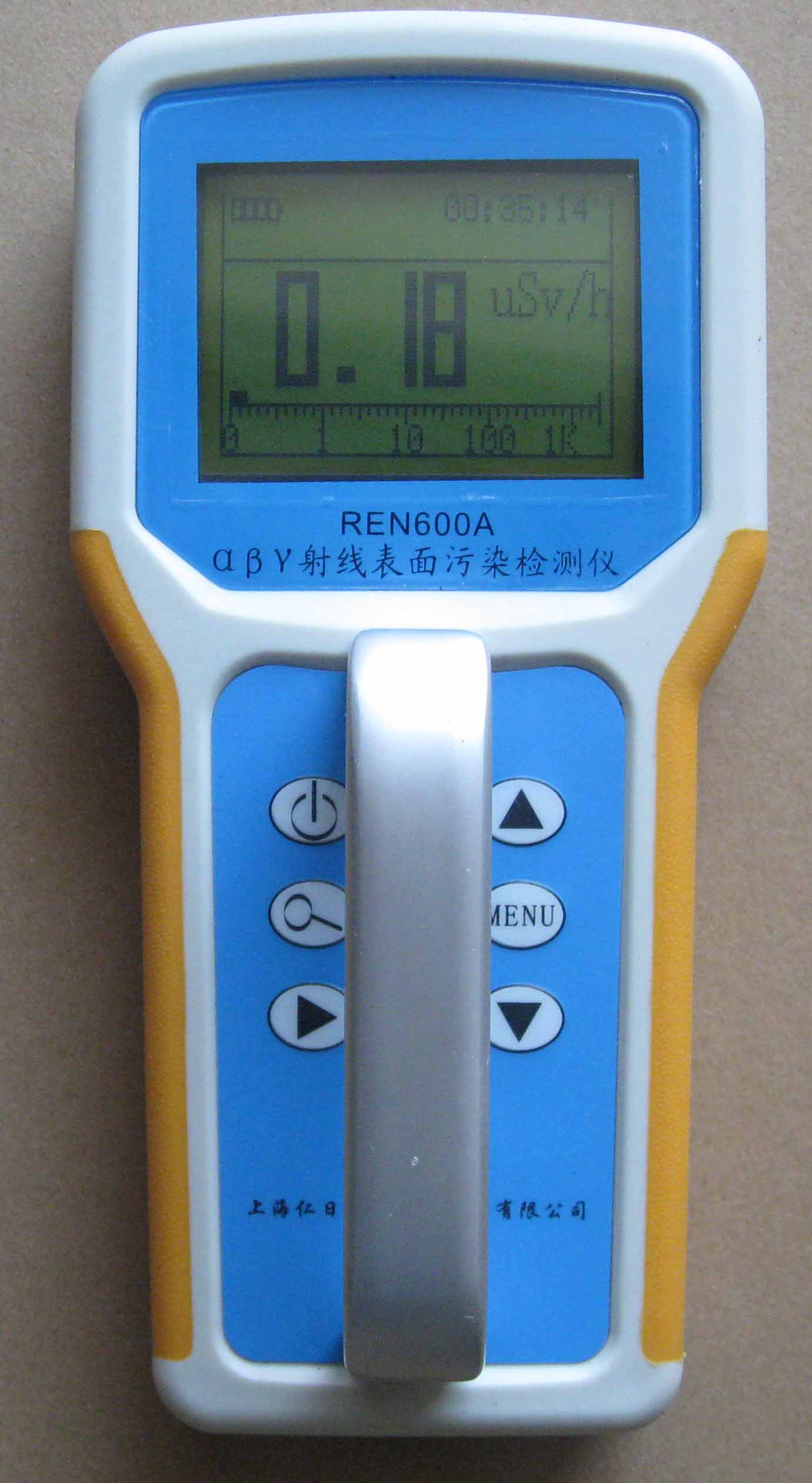
 REN600A型α、β、γ射線表面污染檢測儀即可檢測α、β、γ射線,也能檢測到X射線,它采用高速嵌入式微處器作為數據處理單元,點陣式大屏幕LCD液晶顯示,讀數清晰、操作方便,具有400條超大容量數據存儲。儀器采用進口的大面積MICA蓋革探測器,具有較高探測效率,可進行α、β輻射表面污染檢測和X、γ輻
REN600A型α、β、γ射線表面污染檢測儀即可檢測α、β、γ射線,也能檢測到X射線,它采用高速嵌入式微處器作為數據處理單元,點陣式大屏幕LCD液晶顯示,讀數清晰、操作方便,具有400條超大容量數據存儲。儀器采用進口的大面積MICA蓋革探測器,具有較高探測效率,可進行α、β輻射表面污染檢測和X、γ輻 REN320立柱式X、γ輻射環境監測儀主要用于放射性監測場所的行人或行包通過的監測系統,采用大體積的閃爍體探測器作為探測器,具有體積小,便于攜帶,靈敏度高,誤差小的特點,適用與核應急等特殊的放射性檢測場合。該輻射儀由一根便攜式立柱和一個REN400型多功能輻射儀主機組成。輻射立柱與探頭之
REN320立柱式X、γ輻射環境監測儀主要用于放射性監測場所的行人或行包通過的監測系統,采用大體積的閃爍體探測器作為探測器,具有體積小,便于攜帶,靈敏度高,誤差小的特點,適用與核應急等特殊的放射性檢測場合。該輻射儀由一根便攜式立柱和一個REN400型多功能輻射儀主機組成。輻射立柱與探頭之 REN系列智能化輻射探頭均可和REN300、REN300A、REN300B系列主機配套使用,也可以單獨配套RenRiArea輻射區域監測軟件使用。且具有RS485/RS232的通訊能力。所有探頭均可單獨外接報警燈,在超閾值的情況下就地給出
REN系列智能化輻射探頭均可和REN300、REN300A、REN300B系列主機配套使用,也可以單獨配套RenRiArea輻射區域監測軟件使用。且具有RS485/RS232的通訊能力。所有探頭均可單獨外接報警燈,在超閾值的情況下就地給出 單聯移動式防護屏風
1、規格尺寸: H×W:1800×900 (mm)2、商品描述: 上部鉛有機玻璃的高度為 H×W:240×240 (mm)3、鉛當量: 鉛玻璃0.5mmPb, 下部分鉛當量為0.5mmpb4、外飾材料:碳素鋼板噴
單聯移動式防護屏風
1、規格尺寸: H×W:1800×900 (mm)2、商品描述: 上部鉛有機玻璃的高度為 H×W:240×240 (mm)3、鉛當量: 鉛玻璃0.5mmPb, 下部分鉛當量為0.5mmpb4、外飾材料:碳素鋼板噴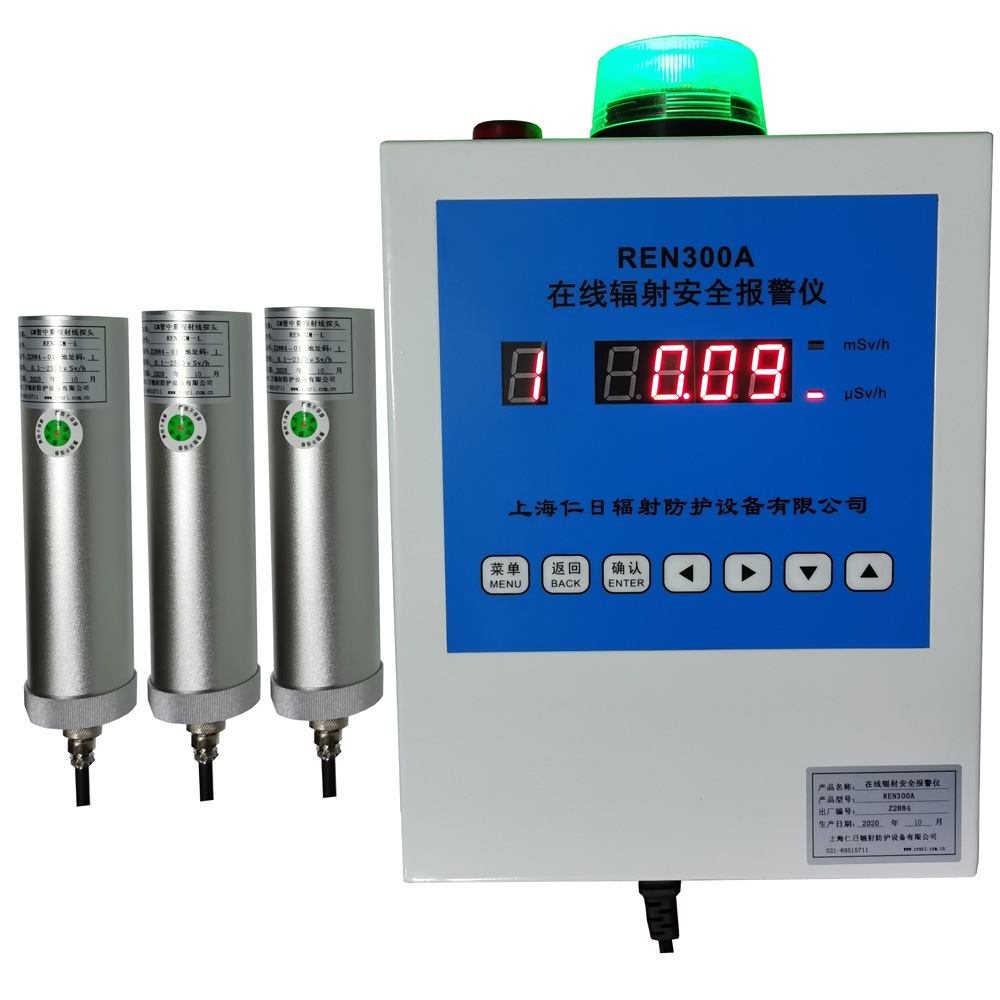 REN300A在線輻射安全報警儀是一種新型的x-γ輻射連續監測報警裝置,它采用特殊設計的前置放大電路,具有靈敏度高、操作方便、自動顯示和超閾值報警等特點,能實時給出xγ輻射劑量率;儀器內置海量數據存儲功能,能存儲10年的歷史數據且標配提供強大的RenLocal輻射監測數據分析軟件。考慮
REN300A在線輻射安全報警儀是一種新型的x-γ輻射連續監測報警裝置,它采用特殊設計的前置放大電路,具有靈敏度高、操作方便、自動顯示和超閾值報警等特點,能實時給出xγ輻射劑量率;儀器內置海量數據存儲功能,能存儲10年的歷史數據且標配提供強大的RenLocal輻射監測數據分析軟件。考慮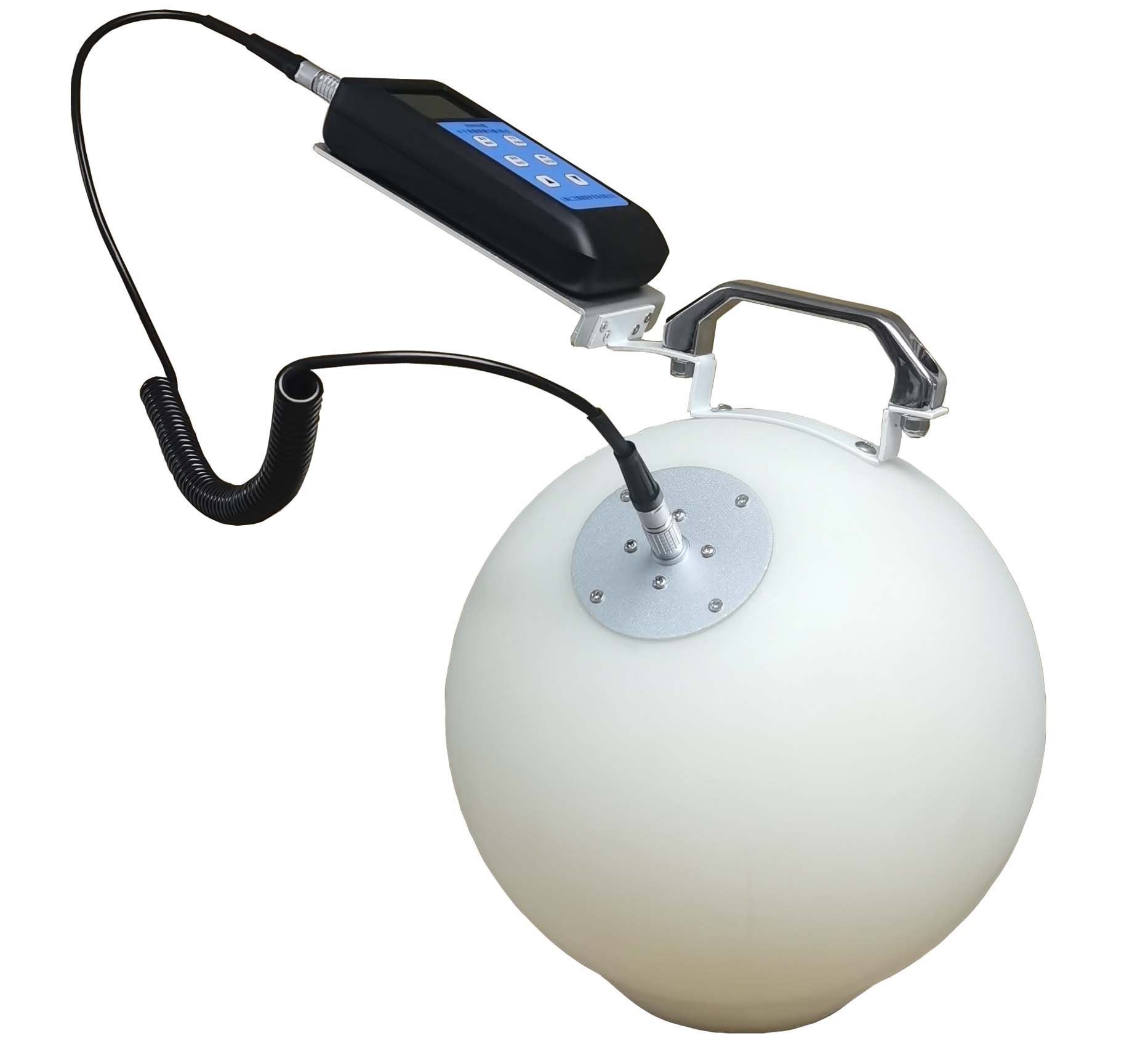 REN800A型中子、X、γ輻射周圍劑量當量(率)儀內置一個進口He-3管和一個GM管作為探測器,能同時檢測中子和X、γ射線。該儀器使用方便;靈敏度高、抗γ性能好、能量響應特性好。此外通過配套的RenRiRate輻射劑量管理軟件可將存儲的數據讀出后分析。該儀器適用于環保、化工、石油、醫療、進出口商檢
REN800A型中子、X、γ輻射周圍劑量當量(率)儀內置一個進口He-3管和一個GM管作為探測器,能同時檢測中子和X、γ射線。該儀器使用方便;靈敏度高、抗γ性能好、能量響應特性好。此外通過配套的RenRiRate輻射劑量管理軟件可將存儲的數據讀出后分析。該儀器適用于環保、化工、石油、醫療、進出口商檢 一、長袖、半袖、無袖射線防護服 1、防護鉛皮:柔軟防護材料; 2、防護性能佳:鉛分布均勻;提供0.35/0.5mmPb鉛當量; 耐磨、易清洗表面材料 3、結構設計:采用多層材料制作,加上專業的人性化結構設計,讓您穿戴舒適; 4、 精密制作工藝:做工精
一、長袖、半袖、無袖射線防護服 1、防護鉛皮:柔軟防護材料; 2、防護性能佳:鉛分布均勻;提供0.35/0.5mmPb鉛當量; 耐磨、易清洗表面材料 3、結構設計:采用多層材料制作,加上專業的人性化結構設計,讓您穿戴舒適; 4、 精密制作工藝:做工精 REN200A型X、γ輻射個人劑量當量HP(10)監測儀(簡稱:個人劑量報警儀)內置高靈敏度蓋格計數管為探測器,主要用來監測各種放射性工作場所的X、γ以及硬β射線的輻射,具有響應快,測量范圍寬的特點。能顯示工作場所的劑量當量率和累積劑量,更換電池時,日期及累積數據能永久保存。可選配RenRiPers
REN200A型X、γ輻射個人劑量當量HP(10)監測儀(簡稱:個人劑量報警儀)內置高靈敏度蓋格計數管為探測器,主要用來監測各種放射性工作場所的X、γ以及硬β射線的輻射,具有響應快,測量范圍寬的特點。能顯示工作場所的劑量當量率和累積劑量,更換電池時,日期及累積數據能永久保存。可選配RenRiPers
氡被稱為“導致人類肺癌的第二大‘殺手’
2006/9/9 10:05:00
氡從何處來?
室內氡的來源是多途徑的,但主要是:
1、巖石(土壤)是室內氡積累的普遍而直接的來源,而且是主要的來源(當居室中各類建材的放射性符合國家標準時)。
2、構造帶。構造帶不是直接的氡來源,但它是地下氡匯集和遷移的通道,有時比巖石因素更重要。例如某地房屋建在裂隙不很發育的花崗巖上,在相同的其他建材條件下,室內的氡往往要比房屋建在放射性較低,而裂隙發育又相當厲害的砂巖上為低。
3、水源有時也是室內氡的重要來源,直接來自地下的、鈾礦區或油氣田區的水往往有較高的氡濃度。
4、在房屋基底經完好密封時,墻地磚的放射性就成了室內氡的主要來源。
5、煤氣通常稱液化氣或天然氣,往往有著相對高的氡濃度。
氡對人體的主要傷害是什么?
專家們把氡稱為“導致人類肺癌的第二大‘殺手’”,是除吸煙以外引起肺癌的第二大因素。世界衛生組織把氡列為使人致癌的19種物質之一。
如何降低居室中的氡?
1、不要購買建筑在富鈾區、伽瑪高值區、斷裂構造區的樓宇。要知道室內的氡含量是否超標,最有效的方法就是進行室內氡濃底的檢測,個人購買住房時,也應考慮這個因素。
2、在裝飾裝修時,要盡量按照國家標準選用放射性含量低的建筑和裝飾材料。
3、室內裝飾中,要注意填平、密封地板和墻上的所有裂縫,特別是地下室、一層和平房的住戶更要如此。
4、做好室內通風換氣,這是最簡便、最省錢的方法。門窗關閉的房屋內,氡的濃度往往比敞開門窗時高數倍到數十倍。專家曾做過試驗,一間氡濃度在151貝可/m3 房間,開窗1小時后,室內氡濃度可降為48貝可/m3。如果配備優質的室內空氣凈化器更好。
5、孩子與婦女比成年男性更易受氡侵害,應盡量減少或禁止在室內吸煙。
國外相關報道:
美國環保署:http://www.epa.gov/radon/healthrisks.html
Exposure to Radon Causes Lung Cancer In Non-smokers and Smokers Alike
Lung cancer kills thousands of Americans every year. The untimely deaths of Peter Jennings and Dana Reeve have raised public awareness about lung cancer, especially among people who have never smoked. Smoking, radon, and secondhand smoke are the leading causes of lung cancer. Although lung cancer can be treated, the survival rate is one of the lowest for those with cancer. From the time of diagnosis, between 11 and 15 percent of those afflicted will live beyond five years, depending upon demographic factors. In many cases lung cancer can be prevented; this is especially true for radon.
Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. Smoking causes an estimated 160,000* deaths in the U.S. every year (American Cancer Society, 2004). And the rate among women is rising. On January 11, 1964, Dr. Luther L. Terry, then U.S. Surgeon General, issued the first warning on the link between smoking and lung cancer. Lung cancer now surpasses breast cancer as the number one cause of death among women. A smoker who is also exposed to radon has a much higher risk of lung cancer.
Radon is the number one cause of lung cancer among non-smokers, according to EPA estimates. Overall, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer. Radon is responsible for about 21,000 lung cancer deaths every year. About 2,900 of these deaths occur among people who have never smoked. On January 13, 2005, Dr. Richard H. Carmona, the U.S. Surgeon General, issued a national health advisory on radon. Visit www.cheec.uiowa.edu/misc/radon.html7 for more on a study by Dr. William Field on radon-related lung cancer in women.
Secondhand smoke is the third leading cause of lung cancer and responsible for an estimated 3,000 lung cancer deaths every year. About 1,000 of these are people that never smoked, and about 2,000 are former smokers. Smoking affects non-smokers by exposing them to secondhand smoke. Exposure to secondhand smoke can have serious consequences for children’s health, including asthma attacks, affecting the respiratory tract (bronchitis, pneumonia), and may cause ear infections.
Learning more about lung cancer. The following sources provide a wide range of good information about lung cancer, prevention, and treatment.
Why is radon the public health risk that it is?
EPA estimates that about 20,000 lung cancer deaths each year in the U.S. are radon-related. Exposure to radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. Radon is an odorless, tasteless and invisible gas produced by the decay of naturally occurring uranium in soil and water. Radon is a form of ionizing radiation and a proven carcinogen. Lung cancer is the only known effect on human health from exposure to radon in air. Thus far, there is no evidence that children are at greater risk of lung cancer than are adults.
Radon in air is ubiquitous. Radon is found in outdoor air and in the indoor air of buildings of all kinds. EPA recommends homes be fixed if the radon level is 4 pCi/L (pico Curies per Liter) or more. Because there is no known safe level of exposure to radon, EPA also recommends that Americans consider fixing their home for radon levels between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L. The average radon concentration in the indoor air of America’s homes is about 1.3 pCi/L. It is upon this level that EPA based its estimate of 20,000 radon-related lung cancers a year upon. It is for this simple reason that EPA recommends that Americans consider fixing their homes when the radon level is between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L. The average concentration of radon in outdoor air is .4 pCi/L or 1/10th of EPA’s 4 pCi/L action level.
For smokers the risk of lung cancer is significant due to the synergistic effects of radon and smoking. For this population about 62 people in a 1,000 will die of lung-cancer, compared to 7.3 people in a 1,000 for never smokers. Put another way, a person who never smoked (never smoker) who is exposed to 1.3 pCi/L has a 2 in 1,000 chance of lung cancer; while a smoker has a 20 in 1,000 chance of dying from lung cancer. Figure A compares the risks between smokers and never smokers; smokers are at a much higher risk than never smokers, e.g., at 8 pCi/L the risk to smokers is six times the risk to never smokers.
The radon health risk is underscored by the fact that in 1988 Congress added Title III on Indoor Radon Abatement to the Toxic Substances Control Act. It codified and funded EPA’s then fledgling radon program. Also that year, the Office of the U.S. Surgeon General issued a warning about radon urging Americans to test their homes and to reduce the radon level when necessary (U.S. Surgeon General).
Unfortunately, many Americans presume that because the action level is 4 pCi/L, a radon level of less than 4 pCi/L is ‘safe’. This perception is altogether too common in the residential real estate market. In managing any risk, we should be concerned with the greatest risk. For most Americans, their greatest exposure to radon is in their homes; especially in rooms that are below grade (e.g., basements), rooms that are in contact with the ground and those rooms immediately above them.
Radon Risk If You Smoke
| Radon Level | If 1,000 people who smoked were exposed to this level over a lifetime*... | The risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to**... | WHAT TO DO: Stop smoking and... |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 pCi/L | About 260 people could get lung cancer | 250 times the risk of drowning | Fix your home |
| 10 pCi/L | About 150 people could get lung cancer | 200 times the risk of dying in a home fire | Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L | About 120 people could get lung cancer | 30 times the risk of dying in a fall | Fix your home |
| 4 pCi/L | About 62 people could get lung cancer | 5 times the risk of dying in a car crash | Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L | About 32 people could get lung cancer | 6 times the risk of dying from poison | Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3 pCi/L | About 20 people could get lung cancer | (Average indoor radon level) | (Reducing radon levels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L | About 3 people could get lung cancer | (Average outdoor radon level) | |
| Note: If you are a former smoker, your risk may be lower. pCi/L (pico Curies per Liter) * Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003). ** Comparison data calculated using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention''s 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Reports. | |||
Radon Risk If You''ve Never Smoked
| Radon Level | If 1,000 people who never smoked were exposed to this level over a lifetime*... | The risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to**... | WHAT TO DO: |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 pCi/L | About 36 people could get lung cancer | 35 times the risk of drowning | Fix your home |
| 10 pCi/L | About 18 people could get lung cancer | 20 times the risk of dying in a home fire | Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L | About 15 people could get lung cancer | 4 times the risk of dying in a fall | Fix your home |
| 4 pCi/L | About 7 people could get lung cancer | The risk of dying in a car crash | Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L | About 4 person could get lung cancer | The risk of dying from poison | Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3 pCi/L | About 2 people could get lung cancer | (Average indoor radon level) | (Reducing radon levels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L | (Average outdoor radon level) | ||
| Note: If you are a former smoker, your risk may be higher. pCi/L (pico Curies per Liter) * Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003). ** Comparison data calculated using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention''s 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Reports. | |||
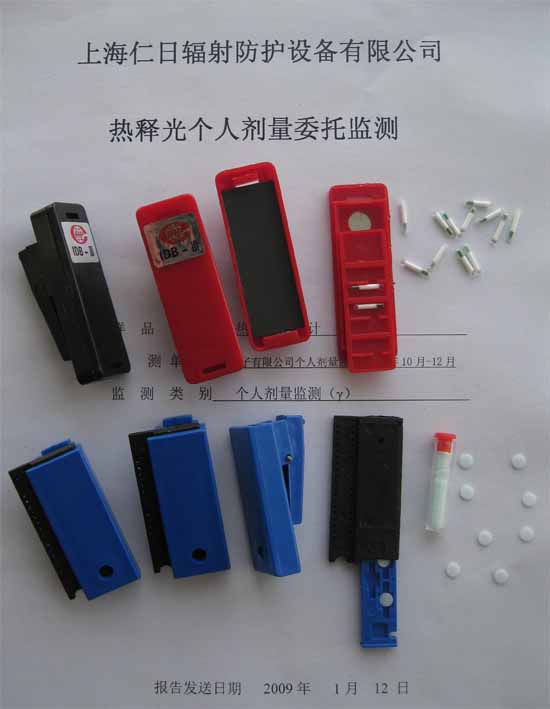
產品名稱:中子及X、γ、β外照射個人劑量監測服務
產品描述:放射工作人員個人劑量委托監測服務 依據《GB18871-2002電離輻射防護與輻射源安全基本標準》和《GBZ128-2002職業性外照射個人監測規范》的要求,以熱釋光個人劑量計作為監測手段,為放射工作人員提供個人劑量委托監測服務,并為企業或衛生行政部
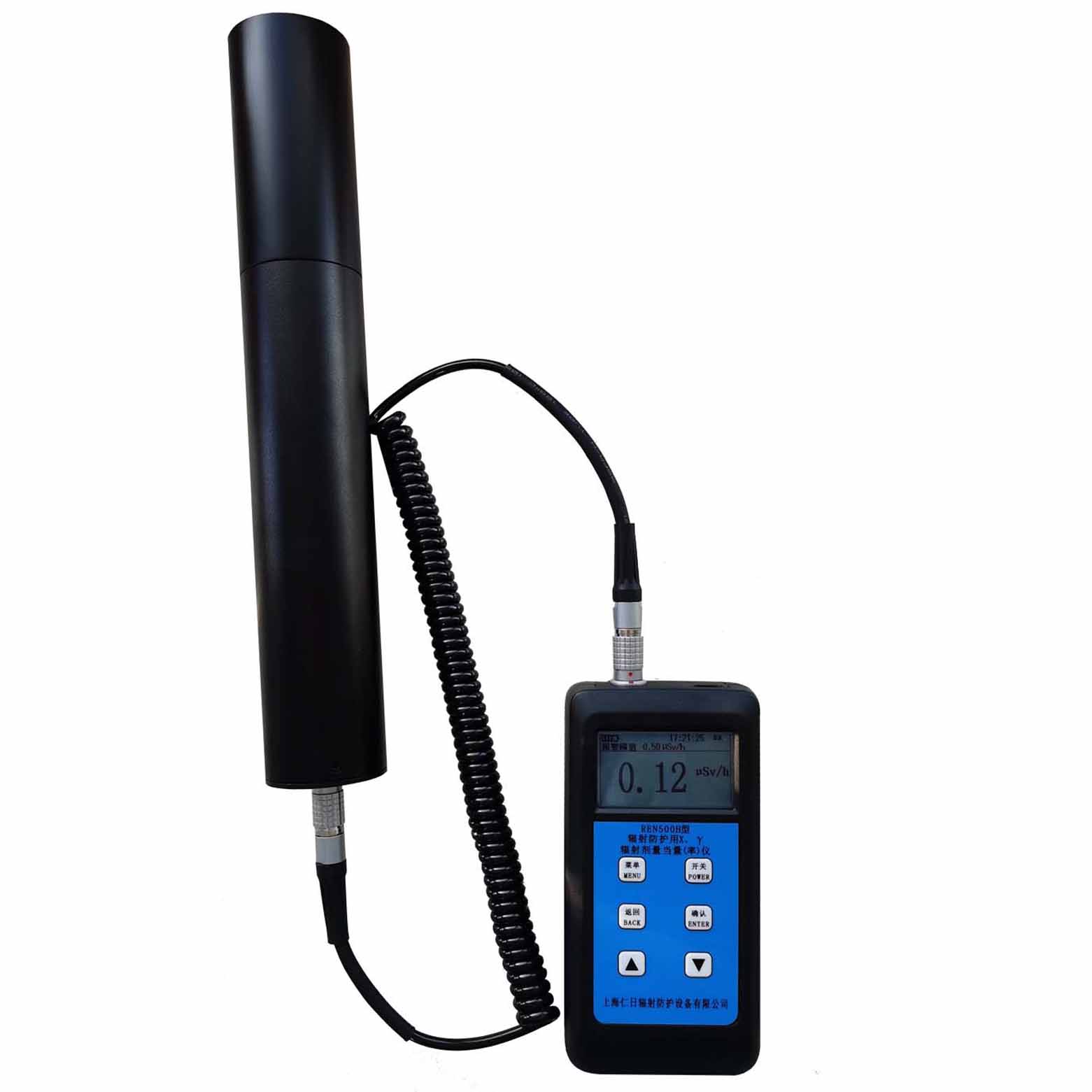
產品名稱:REN500H輻射防護用X、γ輻射劑量當量(率)儀
產品描述:REN500H輻射防護用X、γ輻射劑量當量(率)儀是監測各種高劑量放射性工作場所的輻射劑量率專用儀器。儀器滿足《環境地表γ輻射劑量率測定規范》中高劑量部分的要求。該儀器除能測高能γ射線外,還能對低能X射線進行準確的測量,具有良好的能量響應特性。此外通過配套的RenRiRate輻射劑量管理軟件可將存儲
產品名稱:REN600型α、β表面污染測量儀
產品描述: REN600Bα、β表面污染檢測儀采用閃爍探測法,用來檢測放射性工作場所和實驗室的工作臺面、地板、墻面、手、衣服、鞋等表面受α或β(γ)放射性污染的程度,也可對密封型α、β同位素泄漏水平進行檢測。儀器具有較高的探測效率;此外通過配套的 RenRiRate輻射劑量管理軟件可將存儲的數據讀
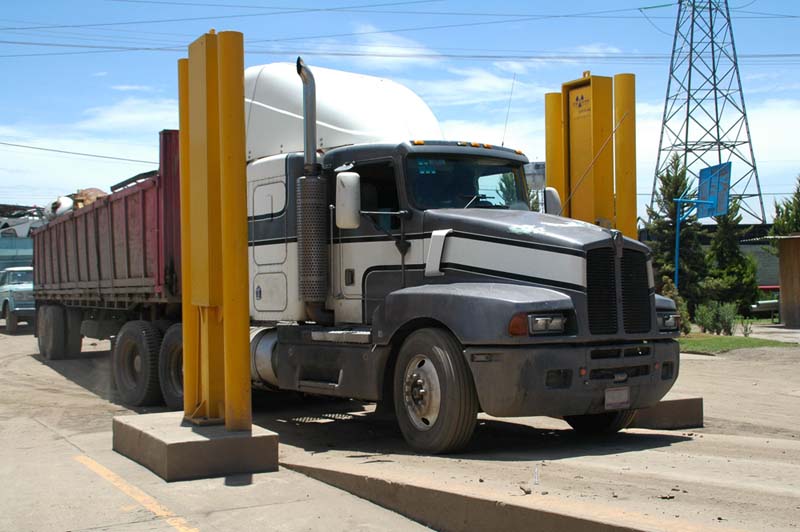
產品名稱:REN700型通道式車輛放射性檢測系統
產品描述:簡介: REN700型通道式車輛放射性檢測系統是用于對通過通道的卡車、集裝箱等車輛內運輸物品的放射性污染及輻射泄露水平的全天候探測系統。該系統具有靈敏度高、探測范圍廣、響應時間短等特點,可實現自動輻射報警、自動數據存儲、自動抓拍通過車輛照片等功能。主要安裝在核
產品名稱:REN200B型X-γ個人劑量報警儀
產品描述:REN200B型X、γ輻射個人劑量當量HP(10)監測儀(簡稱:個人劑量報警儀)內置高量程蓋格計數管為探測器,主要用來監測各種放射性工作場所的X、γ以及硬β射線的輻射,具有較寬的測量范圍。能顯示工作場所的劑量當量率和累積劑量,更換電池時,日期及累積數據能永久保存。可選配RenRiPersonal個人
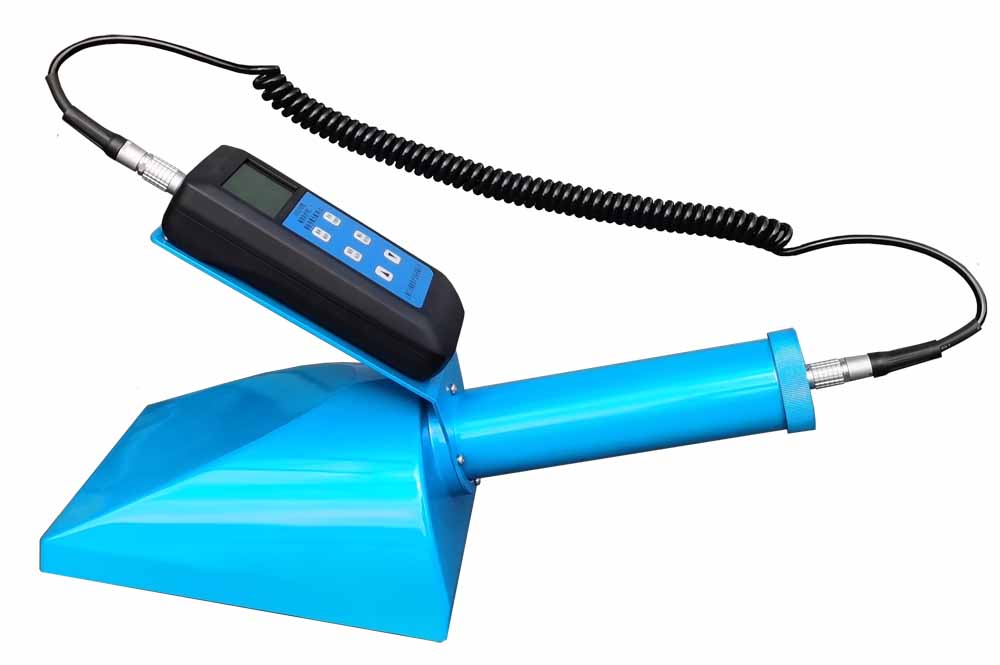
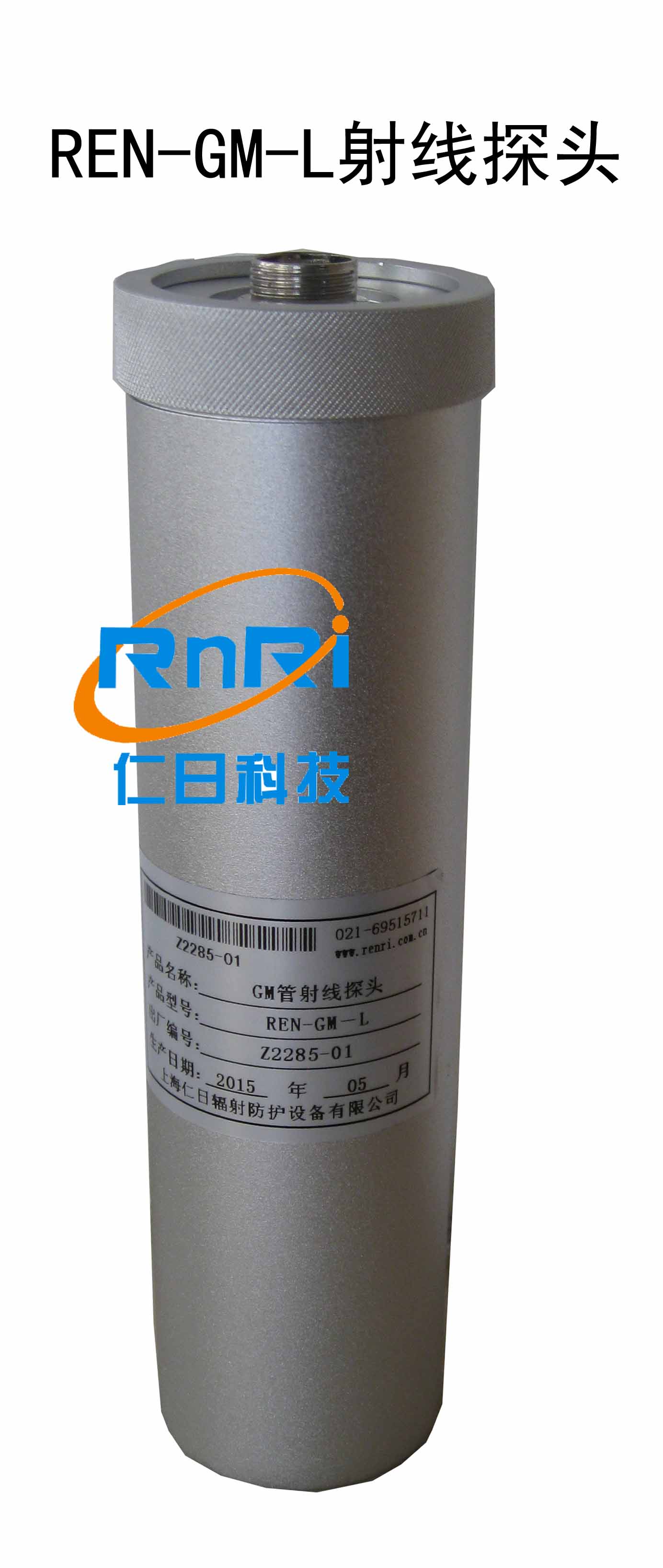
產品名稱:REN-GM-L型GM管中量程射線探頭
產品描述:REN系列智能化輻射探頭均可和REN300、REN300A、REN300B系列主機配套使用,也可以單獨配套RenRiArea輻射區域監測軟件使用。且具有RS485/RS232的通訊能力。所有探頭均可單獨外接報警燈,在超閾值的情況下就地給出聲光報警。 1、測量射線類型:X、γ射線2、探測器:GM管探